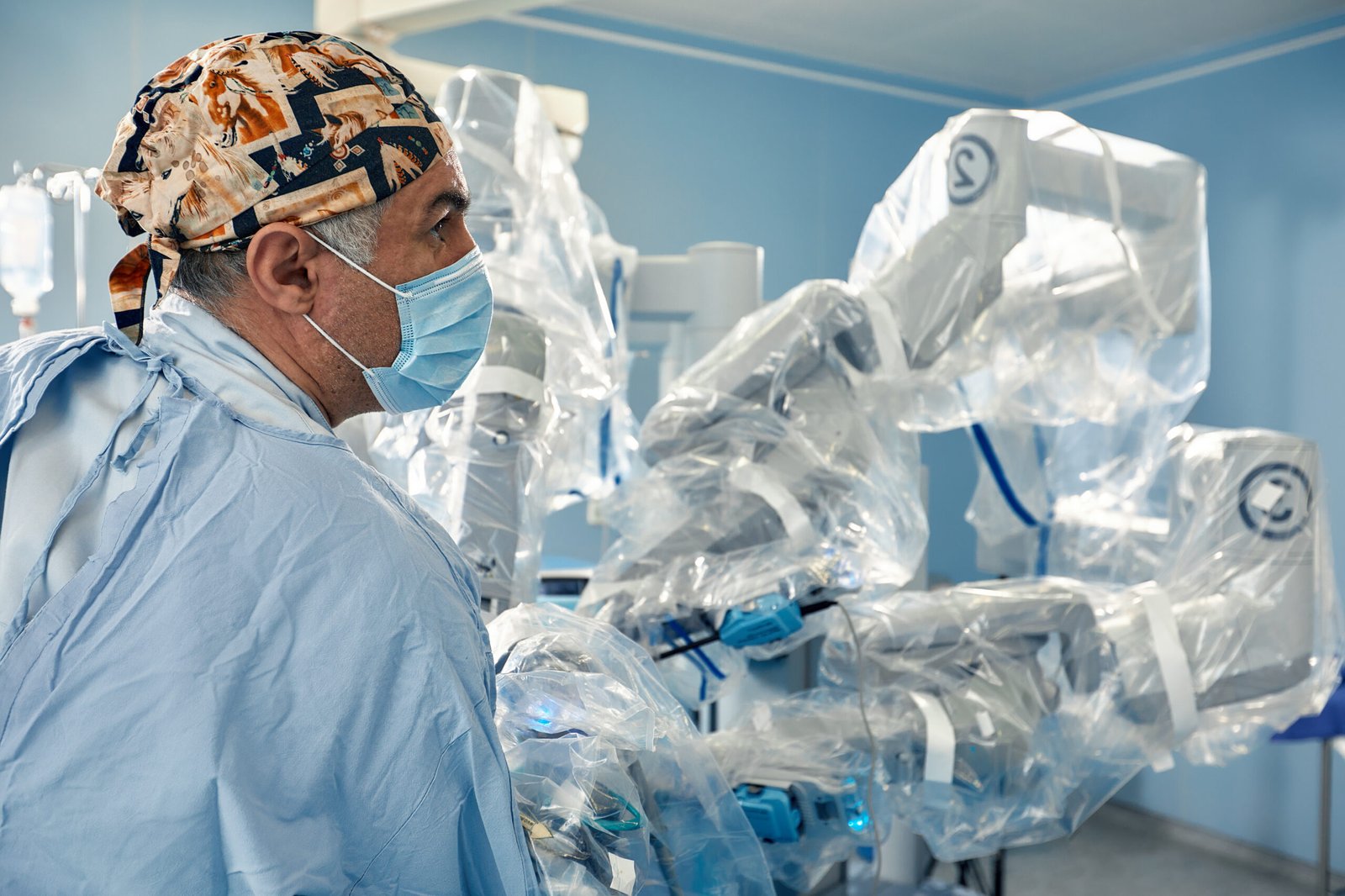
The field of cosmetic surgery is evolving rapidly, with technological advancements redefining how procedures are performed and enhancing patient outcomes. One of the most significant breakthroughs in recent years is robotic-assisted surgery, which provides unmatched precision, consistency, and control. Originally developed for complex medical procedures, robotic systems are now being adapted for aesthetic treatments, offering both surgeons and patients new possibilities in cosmetic enhancement.
This article explores the role of robotic-assisted surgery in aesthetic medicine, its applications in various procedures, and the benefits it offers in terms of safety, precision, and recovery. As this technology advances, it is setting new standards for surgical excellence and patient satisfaction.
What Is Robotic-Assisted Surgery?
Robotic-assisted surgery involves the use of computer-controlled robotic systems that enhance a surgeon’s capabilities, allowing for intricate and precise movements. Unlike fully autonomous systems, these robotic platforms do not operate independently but are controlled by the surgeon, ensuring meticulous adjustments tailored to each patient’s anatomy.
In aesthetic medicine, robotic-assisted systems are particularly valuable for procedures requiring detailed adjustments, symmetry, and consistency. The integration of high-definition imaging, artificial intelligence (AI), and haptic feedback allows for unparalleled accuracy, improving both surgical efficiency and patient satisfaction.
How Robotic-Assisted Systems Work
Robotic surgical platforms combine several cutting-edge technologies to enhance the precision and safety of cosmetic procedures:
Robotic Arms – Mimic the surgeon’s hand movements with exceptional precision, minimising the risk of human error.
AI-Driven Surgical Planning – Analyses patient anatomy to optimise implant placement and contouring techniques.
High-Definition 3D Imaging – Provides magnified and detailed visualisation of the treatment area, enabling more accurate adjustments.
Haptic Feedback Mechanisms – Improve control and sensitivity, allowing surgeons to perform delicate refinements with confidence.
These advancements allow for a level of surgical precision that is difficult to achieve with traditional manual techniques, enhancing the predictability and consistency of results.
Applications of Robotic-Assisted Cosmetic Surgery
Robotic systems are now being incorporated into various cosmetic procedures, offering significant benefits across different treatment areas.
1. Hair Restoration Surgery
Robotic-assisted follicular unit extraction (FUE) is transforming hair transplantation by improving the accuracy of follicle selection and placement. The system precisely extracts and implants grafts, ensuring natural growth patterns and reducing trauma to the surrounding scalp. Patients benefit from minimal discomfort, faster recovery, and a significantly improved success rate.
2. Body Contouring and Liposuction
High-definition liposuction and body sculpting procedures are benefiting from robotic-assisted technology. AI-guided fat removal enables precise contouring, achieving smoother and more symmetrical results. Additionally, robotic systems help preserve surrounding tissues, leading to less swelling, reduced downtime, and a lower risk of post-surgical complications.
3. Facial Rejuvenation and Rhinoplasty
For procedures like facelifts and rhinoplasty, robotic-assisted technology allows for micro-adjustments with extreme precision. The system’s real-time imaging enhances proportional symmetry, creating more balanced and natural-looking results. Surgeons can also make refined modifications based on the patient’s specific aesthetic goals, improving the predictability of outcomes.
4. Breast Reconstruction and Augmentation
Robotic-assisted surgery is increasingly being used in breast reconstruction and augmentation procedures. The system allows for more accurate implant placement, minimising scarring and reducing post-operative complications. This approach is particularly beneficial for reconstructive surgery following mastectomies, offering enhanced aesthetic and functional results.
5. Emerging Non-Invasive Applications
Research is underway to explore robotic applications in non-invasive aesthetic treatments, such as laser therapy, skin tightening, and minimally invasive facial procedures. These advancements could broaden the appeal and accessibility of robotic-assisted treatments in the near future.
The Benefits of Robotic-Assisted Cosmetic Surgery
The integration of robotic-assisted systems into cosmetic surgery offers a range of advantages for both surgeons and patients:
Enhanced Precision – Eliminates human tremors, ensuring flawless execution of complex procedures.
Reduced Scarring and Downtime – Enables smaller incisions and minimally invasive techniques, leading to faster healing.
Consistent and Predictable Results – Robotic systems standardise procedures, reducing variability and enhancing outcome reliability.
Improved Visualisation – High-definition imaging allows surgeons to see fine anatomical details, improving decision-making.
Ergonomic Support for Surgeons – Reduces physical strain on surgeons, enabling longer and more intricate procedures with sustained precision.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many benefits, robotic-assisted surgery faces certain challenges:
High Initial Costs – The expense of acquiring and maintaining robotic systems can be prohibitive for smaller clinics.
Specialist Training Required – Surgeons must undergo advanced training to operate robotic platforms effectively.
Limited Accessibility – Availability is currently restricted to select clinics with the necessary infrastructure.
However, as robotic technology continues to evolve and become more cost-effective, accessibility and affordability are expected to improve.
The Future of Robotic-Assisted Surgery in Aesthetics
The future of robotic-assisted cosmetic surgery is promising, with several emerging trends shaping its evolution:
Miniaturisation of Robotic Systems – Making the technology more accessible to smaller clinics and independent practitioners.
AI-Driven Customisation – Utilising AI algorithms to tailor procedures based on individual patient characteristics.
Expanded Non-Invasive Applications – Research into scar revision, skin rejuvenation, and injectables.
Cost Reduction Through Wider Adoption – As demand grows, technological advancements will likely drive costs down, making robotic-assisted procedures more widely available.
Conclusion
Robotic-assisted surgery is revolutionising the field of cosmetic surgery, enhancing precision, improving safety, and optimising patient outcomes. By leveraging AI, real-time imaging, and robotic precision, these systems are redefining what is possible in aesthetic medicine.
While challenges such as cost and training remain, ongoing advancements are expected to make robotic-assisted surgery more accessible in the future. For patients in the UK considering cosmetic procedures, this technology offers an opportunity to achieve their aesthetic goals with greater confidence, minimal downtime, and superior results.
As robotic systems continue to evolve, they are set to become an integral part of modern cosmetic surgery, offering transformative possibilities for both patients and practitioners.