Introduction
Cognitive health refers to the functionality of the brain encompassing memory, reasoning, and completing daily activities. Cognitive health is important in a person’s overall health and brain function. While genetics and physical factors such as exercising and sleeping well have a major influence on brain functioning, studies are beginning to showcase the impact that diet has towards brain health. Recent research indicates that there is an increased likelihood of red meat consumption leading to processed cognitive decline and dementia. On the other hand, a Mediterranean diet seems to positively conserve brain health by sustaining white matter integrity on the brain. Knowing how different people’s nutrition affects an individual’s cognition may enable such people make dietary decisions after understanding the consequences of their actions on their mental acuity in old age.
Considering that the brain uses a significant amount of energy, it needs a constant stream of nutrients to keep functioning at an optimal level. Deficient eating behaviors in people may lead to inflammation, oxidative stress, and cognitive impairment which can be damaging to the blood vessels. Additionally, a diet that consists of a lot of nutrients can aid by providing people with the important vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help to aid in the protection of the neurons and synaptic communication.
Enhance or impair cognitive function due to some dietary choices. Processed red meats as well as refined sugars, and saturated fat have a tendency to enhance inflammation and inflammation in the body, hence resulting in neurodegenerative diseases over time. Healthy diets, however, composed of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats enhance memory functions and overall brain health.
Processed Red Meat and Cognitive Decline
Deli meats, bacon, and sausages, all processed red meats contain preposterous levels of saturated fats, nitrates, and advanced glycation end-products (AGEs). They are some of the things responsible for oxidative stress as well as inflammation that results in cognitive decline.
Studies suggest that excessive consumption of processed meats:
Increases pro-inflammatory cytokines levels, aggravating neurodegeneration.
Cadaverous disease risk increases along with the heart disease due to altered blood circulation to the brain.
Dominates insulin resistance, a condition associated with advancing dementia.
A recent longitudinal study found that individuals who frequently consume processed red meat had a higher likelihood of memory impairment and slower cognitive processing speed.
The Mediterranean Diet And Brain Health
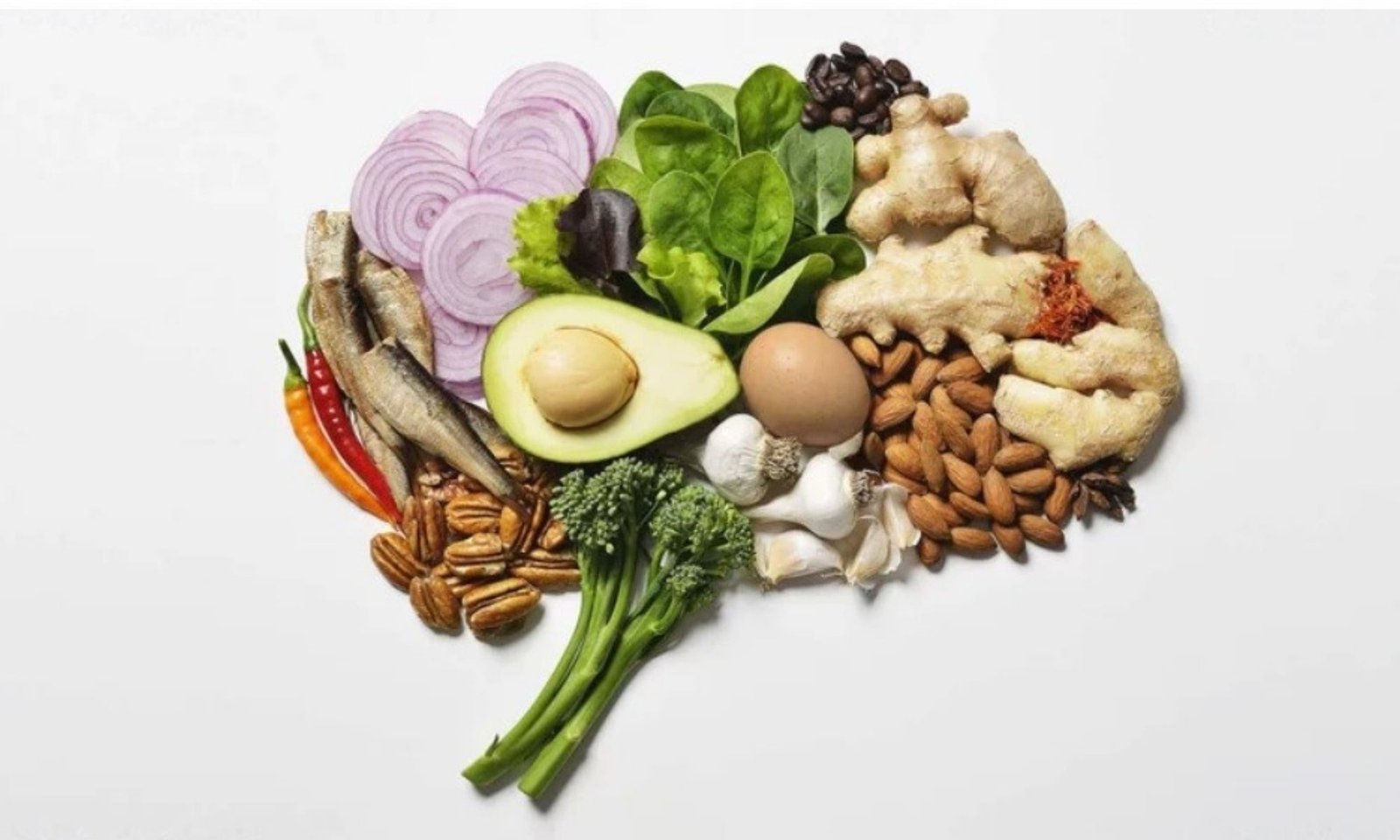
The Mediterranean diet, which includes a great deal of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, olive oil, and fish, has been shown to have great positive effects on cognitive longevity. This dieting pattern contains vital nutrients for the brain, including omega 3 fatty acids, polyphenols, and flavonoids. Omega 3 fatty acids, polyphenols, and flavonoids all aid in the brain’s functioning.
The Mediterranean diet has a lot of benefits and some of them are:
Reduced inflammation: The abundance of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory elements assists with the protection of neurons.
Enhanced blood flow: Omega 3 fatty acids allow for circulation, which guarantees the adequate supply of oxygen in the brain.
Support for neurotransmitters: Important nutrients such as folate, vitamin B12, and choline aid in the synthesis of vital neurotransmitters needed for learning and remembering.
Preservation of white matter integrity: Research has suggested that Mediterranean diet-adhering individuals have better structural integrity of white matter, which is essential for neurocommunication.
Key Nutrients For Cognitive Health
Several of these nutrients are essential in aiding the health of the brain and simultaneously mitigate the risk of cognitive decline:
Omega 3 fatty acids: These acids are found in fish, flaxseed, and walnuts. These omega 3 fatty acids are vital in the development and functioning of the brain.
Antioxidants: Dark chocolate, berries, and green leafy vegetables all contain flavonoids and polyphenols that defend the body against oxidative stress.
B Vitamins: Vital for nerve and cognitive function, B vitamins are available from whole grains, eggs, and legumes.
Magnesium: Found in nuts, seeds, and dark chocolate, magnesium is involved in the activity of some of the neurotransmitters and is important for synaptic plasticity.
The Importance of Gut Health in Cognitive Functioning
Newer studies show that the gut microbiome can influence the brain via the gut-brain axis. A diet high in fibre, probiotics, and prebiotics helps to maintain a healthy gut microbiota, which has a positive impact on cognitive function. Foods like yogurt, kimchi, and kefir help to balance the gut microbiome, decrease inflammation, and promote the production of neurotransmitters aiding cognitive function.
Dietary Changes for Enhanced Brain Health
Brain-friendly eating does not require complete overhauls; rather, small changes can have a significant impact. Here are a few dietary changes that might help:
Diminish the amount of processed red meat consumed and substitute with fish or poultry.
Raise the intake of colourful fruits and vegetables.
Use whole grains such as quinoa, brown rice, and oats instead of white refined grains.
Use healthy fats such as from olive oil, avocado, and nuts.
For optimal hydration and mental clarity, avoid sugary drinks and drink water frequently.
Conclusion
Research dietary patterns and their effects are more and more integrated with quantitative studies of cognition, and they are revealing both positive and negative impacts. The consumption of processed red meats carries an increased risk of cognitive decline, while the Mediterranean diet offers important neuroprotective benefits. With some mindfulness in making appropriate dietary decisions, one can help maintain their brain health while preventing neurodegenerative diseases, which improves the quality of life.