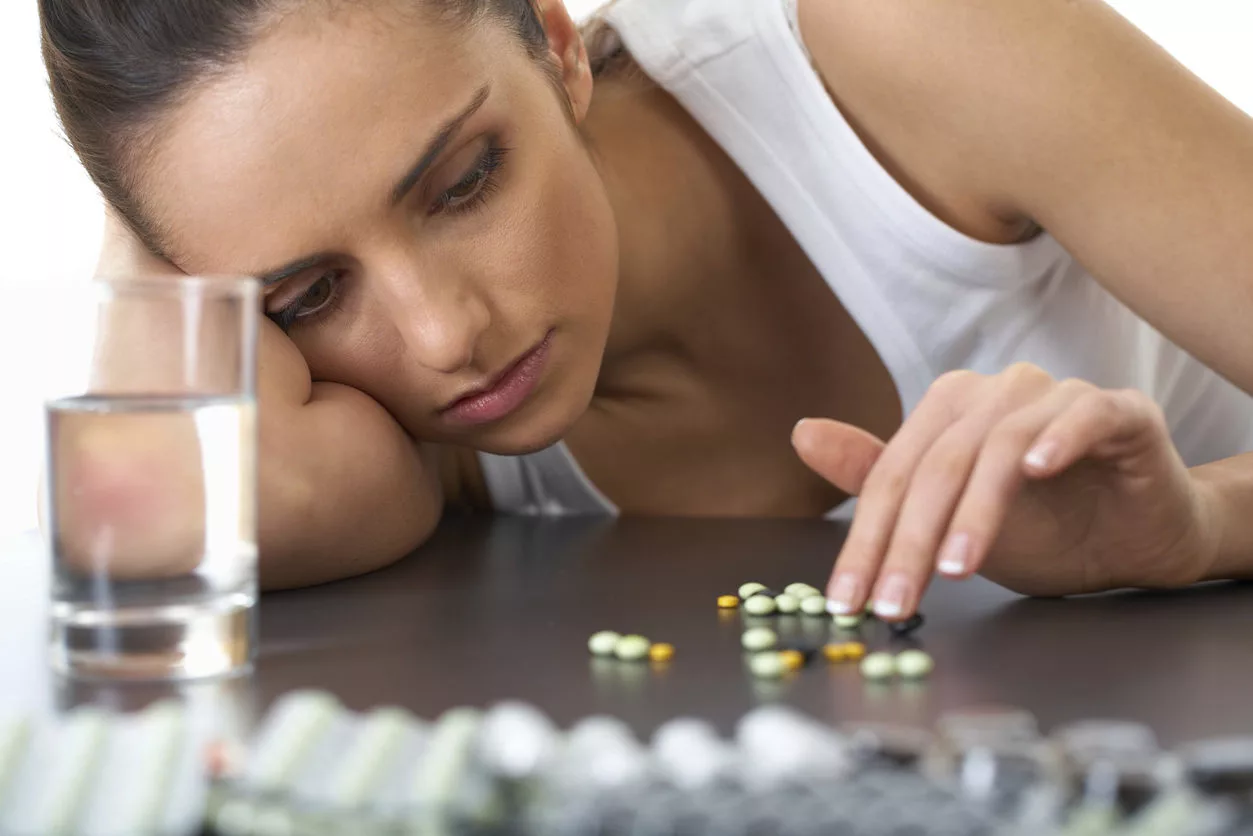
Depression is a well-known issue which over affects millions of people worldwide. The more common treatments have been SSRIs or antidepressants and cognitive behavioral treatment for over 30 years. They offer help, but there are some patients who do not respond to the conventional treatment options. One of them is the approval of Spravato, a nasal spray that is ingested for treatment-resistant depression. In this piece, I will cover the newest developments in depression treatment and how they will change the care of the patients. One of them is the approval of the nasal spray Spravato which offers a new approach for treatment-resistant depression.
Knowing What Treatment-Resistant Depression Is
When a person has tried using a minimum of 2 different types of antidepressants and does not get any relief from the symptoms, such a condition is referred to as Treatment-Resistant Depression. A large number of patients suffering from depression for a very long time, are at a high risk of suicide while suffering from TRD.
These are the factors that make a person prone to Treatment-Resistant Depression (TRD):
- A negative family history due to how the body metabolizes antidepressants
- Medication resistant neurochemical abnormalities
- Other primary health issue/s including hypothyroidism or autoimmune disease/s.
People suffering from TRD usually have to go through a lot of trial-and-error for the right fit for their treatment. Sadly, the process can often be lengthy. Fortunately, emerging technologies are leading to new possibilities in therapeutics.
The Introduction of Esketamine (Spravato)
An example of a novel treatment for depression is the development of esketamine, a ketamine derivative that can be administered by nasal spray. Unlike other antidepressants, which focus on increasing serotonin levels, esketamine has a more complex mechanism of action, targeting N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors and altering glutamate activity.
The uses of esketamine include the following:
- Rapid Onset of Action – Unlike SSRIs, which can take weeks to become effective, esketamine has been shown to alleviate symptoms within hours to days.
- Effectiveness for TRD – Clinical trials have demonstrated patients’ response self-reduction in patients who are not responsive at all to treatment.
- Reduction in Suicidal Thoughts – Some studies found that esketamine has the potential to reduce suicidal thoughts, which may help save a life.
Esketamine is given in a clinic under supervision of a physician because it may cause dissociation and moderate increase in blood pressure.
Therapy with Psychedelics: The Study of Psilocybin
The treatment of depression with psychedelics, particularly psilocybin mushrooms, is proving to be a pivotal and groundbreaking area of research. There is a rising interest in Psilocybin Therapy and its role in inducing neuroplasticity and improving emotional context processing.
Findings from various studies indicate that Psilocybin Therapy has the following beneficial impacts on individuals:
- Results in positive alterations of brain functioning and is correlated with enhanced mood and emotion regulation capacity.
- Increases the efficiency with which a person is able to cope with and process traumatic events.
- May offer relief over an extended duration post a few therapies.
Currently, clinical trials are being conducted to assess the efficacy and safety of psilocybin treatments for patients suffering from major depressive disorder (MDD). Initial outcomes indicate that it would replace traditional antidepressants.
Progress in Treating Neuropsychological Disorders Using Neurostimulation
Pharmacotherapy resistance is becoming an increasingly common phenomenon, alongside drug-resistant depression. Emerging from this is a new field of treatment that includes neurostimulation. Some of these therapies include:
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): A noninvasive technique that directs magnetic fields to the brain’s nerve cells. This method of treatment is effective with patients suffering from TRD, with very few adverse effects.
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): A procedure where a device that is placed superficially under the skin sends electrical signals to the vagus nerve for mood regulation.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): A new method of treating mood disorders which consists of the placement of electrodes within the brain that is thought to control mood regulating neurons.
These therapies offer the possibility of improvement to people who have not benefited from medication treatment on its own.
Influences of Lifestyle and Alternative Therapies
In addition to progression in medicine, an increasing number of people acknowledge personal lifestyle choices and alternative therapies as relevant aspects of depression management. Some of the strategies that have proven to be effective include:
- Nutritional Therapy: Following a Mediterranean diet with whole foods, and food rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, is associated with better mood regulation.
- Physical Activity: The regular taking part in physical exercise has proven to be beneficial in improving the functionality of the brain and the depressed state of an individual.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Several practices including mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) and yoga can enable practitioners to alleviate self-imposed stress and negative thinking patterns.
- Gut Flora and Mental Disorders: Recent studies indicate that gut microbiota may be part of the etiology of mental disorders, and suggest that probiotics and prebiotics may have a positive effect on mood and cognitive functions.
Conclusion
The way depression is treated is continuously advancing, and there is now hope for patients who have had little success in treating their depression with traditional therapies. For example, the use of esketamine nasal spray and the advent of psychedelic therapy and neurostimulation has offered alternative treatment options for patients with treatment-resistant depression. With ongoing research, mental healthcare will surely become more individualized and streamlined in the future.